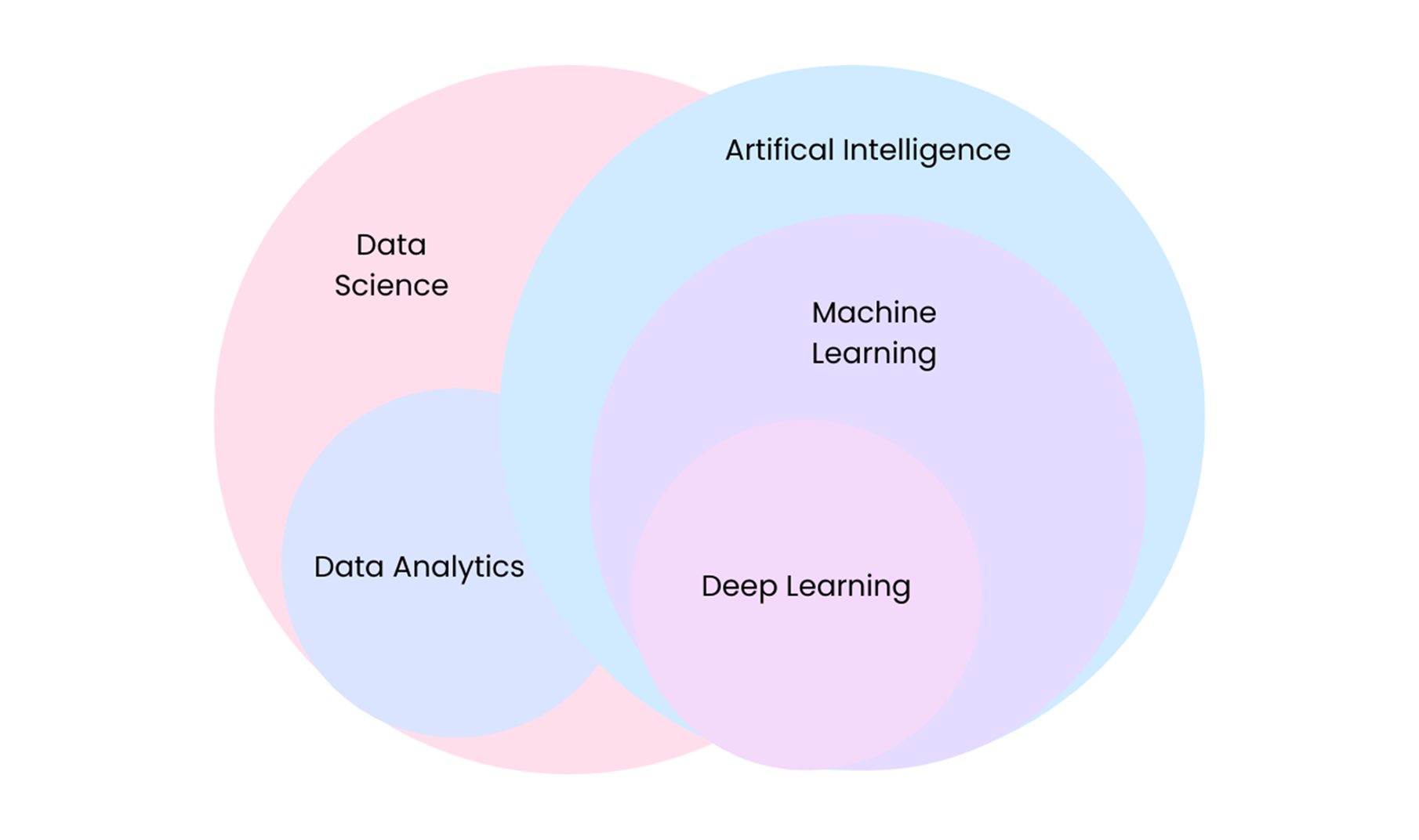
Differences between AI and ML
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is used to describe computers that can simulate human thinking and reasoning abilities. AI uses software programs to perform tasks that usually require human intelligence. They make use of software that can learn and think like humans.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is a sub-set of AI in which computers learn and predict nearly accurate outcomes without being explicitly programmed. A machine learning model continuously learns and refines its performance using data. An ML model can better its performance by feeding in more and more data similar to a human mind using additional data points for an improved learning experience. ML makes use of Deep Learning for continuous learning and development of the ML model.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of ML that uses artificial neural networks to learn and experience from data similar to the human brain. The human brain uses data to learn, experience and make decisions. Deep learning takes its inspiration from the human brain. DL’s artificial neural networks draw parallels with the human brain’s neural network.
Data Science
Data Science (DS) uses data to create models that predict future outcomes. It looks more at the processes for data production and data modelling, creating algorithms and building predictive models. Data Science relates to a wider field that focusses on discovering large sets of data. Discover means – explore data, identify trends, spot anomalies and derive insights.
Data science encompasses data analysis and includes other areas such as data engineering and machine learning. Data scientists use statistical and computational methods to extract insights from data, build predictive models, and develop new algorithms.
Data Analysis
Data Analysis (DA) is a more focussed area within data science that derives meaningful insights using existing data. DA is about analysing existing data and explaining outcomes based on that.
Data Analysis involves analysing present data to gain insights and make informed business decisions. Analysis can make use of AI and ML for predictive analysis and helping businesses to forecast. The integration of AI and ML tools into data analysis signifies a transformative trend. In this era, analysis goes beyond traditional methods, as AI and ML algorithms can automatically identify patterns, trends and anomalies in vast datasets.
Data Engineering
Data Engineering (DE) is the practice of designing and building systems for data collection, storage, transformation, and analysis of large amounts of raw data - structured and unstructured - from multiple sources so that data scientists and analysts can derive valuable insights from it. These systems make data accessible that businesses can then use to thrive.
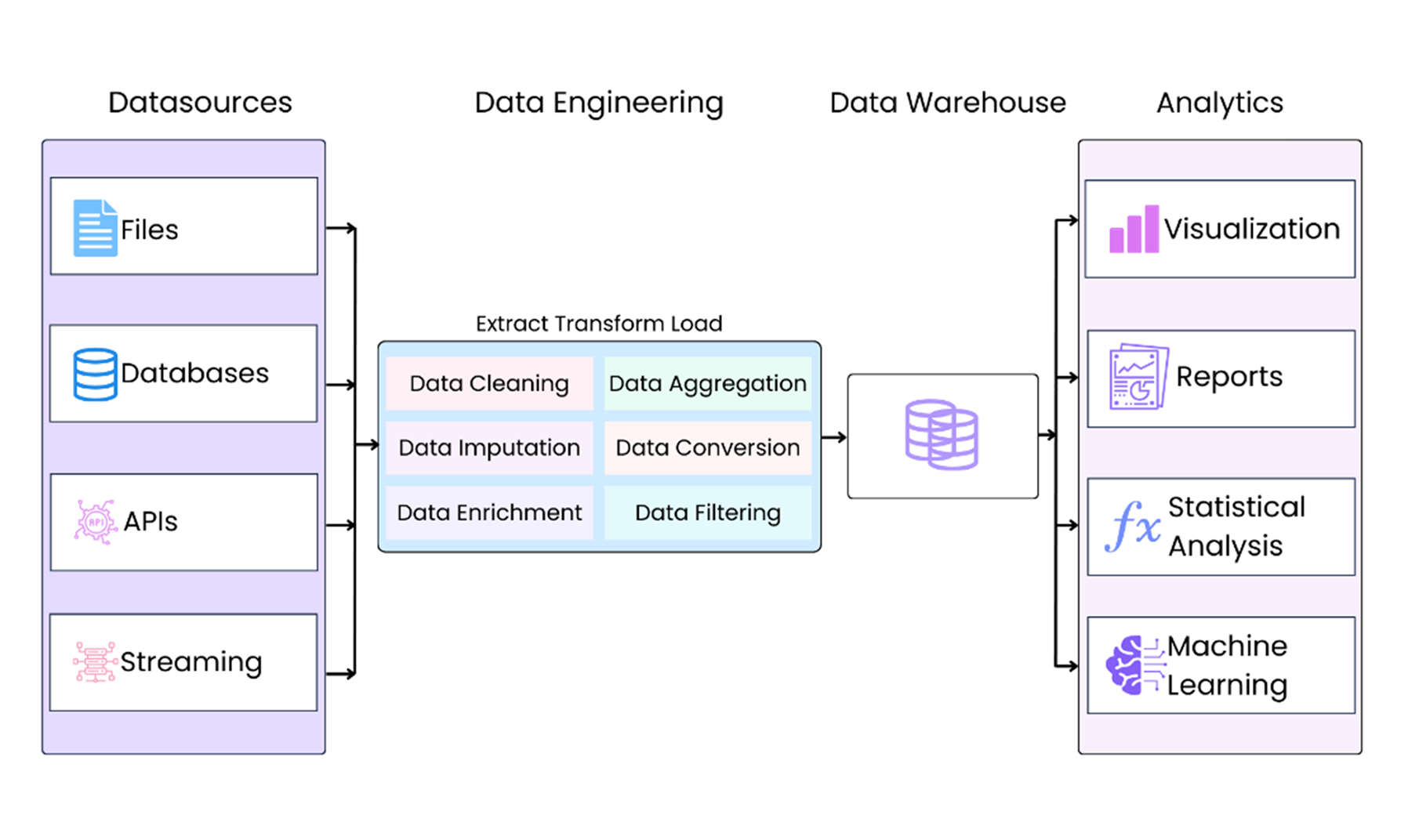
Data Engineering plays a key role in preparing and organizing data for analysis. It involves tasks like data cleaning, data transformation, and data imputation. Data cleaning removes errors and inconsistencies. Data Transformation, which converts data into a usable format. Data Imputation, which fills in missing values, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), where data is gathered, processed, and stored. These steps ensure the data is accurate and ready for decision-making. We will explain each of these activities in more detail in the next sections.
Having understood the differences between the various technological trends, let us now look at the role of a full stack data scientist.