Extract, Transform and Load (ETL)
The ETL process, which stands for Extract, Transform, Load, is a method used to move and process data from different sources into a final system for analysis or storage. It is widely used in data management, particularly in building data warehouses and business intelligence systems.
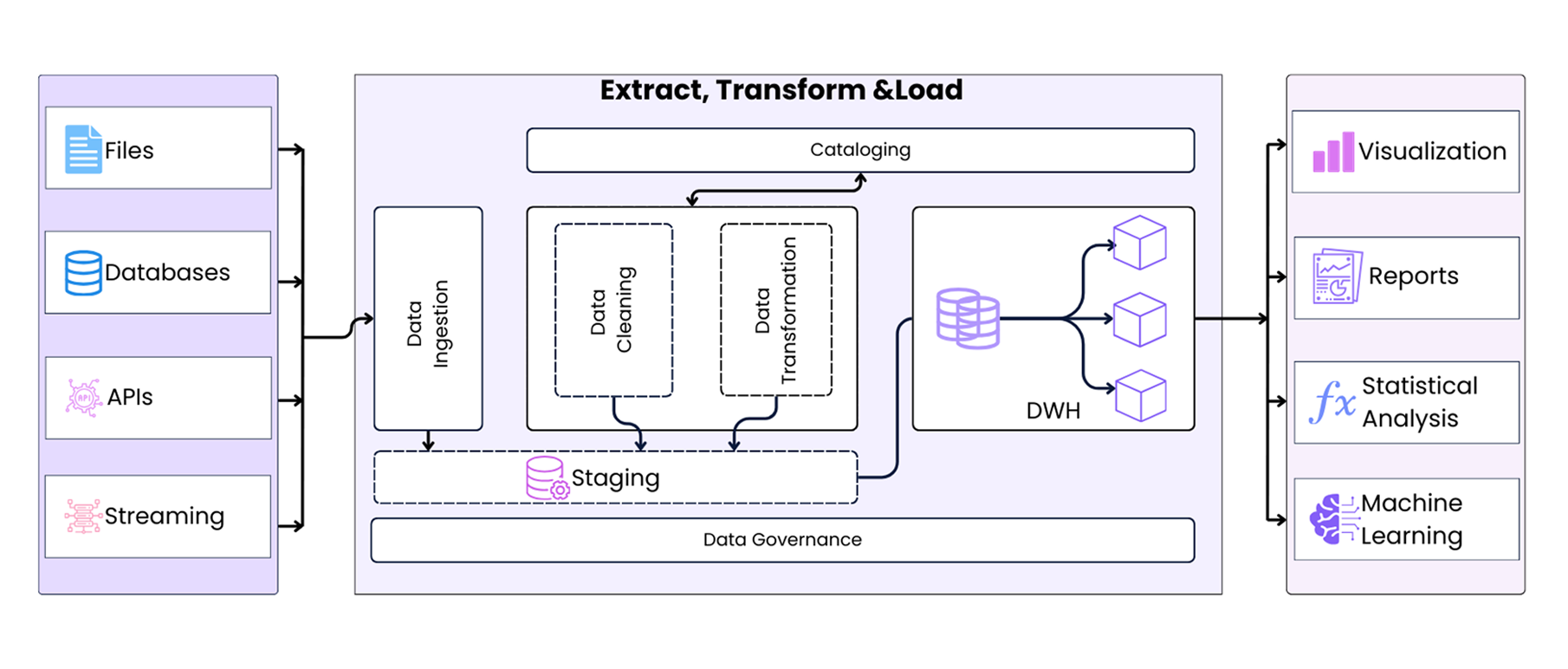
- Extract: This is the first step where we collect data from various sources like databases, files, or APIs.
- Transform: Here, we clean and organize the data. We fix errors, remove duplicates, and format it so it is ready to use. For example, we might convert dates into a standard format or group sales data by region.
- Load: In this step, we take the cleaned and organized data and store it in a data warehouse.
Extract involves pulling data from various sources such as databases, files, or APIs. This ensures that the required data is collected, regardless of the source type. The main challenge in this phase is managing different data formats and preventing any data loss.
Transform cleans and organizes the extracted data to make it usable. This step includes tasks like removing duplicates, correcting errors, and ensuring the data matches a specific format. It also involves adding new information to enrich the dataset. As this phase improves the quality and consistency of the data, it can be time-consuming if the transformation is complex.
Load transfers the transformed data into the target system, such as a data warehouse or analytics platform. This phase involves either batch uploads or real-time uploads, depending on the requirements.
ETL is a powerful tool for managing and using data, but understanding its benefits and challenges helps businesses implement it effectively.
Why is ETL Important?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is crucial for managing and utilizing data effectively. It gathers information from different sources, cleans it, and stores it in a central system for easy access and analysis. Here’s why it matters:
- Collects Data: ETL collects data from various platforms, possibly in various formats and brings it together in one place, into one format, making it easier to use.
- Improves Data Quality: By removing errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies, ETL ensures that the data is reliable.
- Supports Decision-Making: Organized and accurate data helps businesses make informed choices.
- Saves Time: Automation of ETL tasks reduces the time spent on repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on analysis.
- Adapts to Growth: ETL systems scale up to handle increasing amounts of data and new sources.
Evolution of ETL
The evolution of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is more about how businesses have adapted to increasing data needs and advancements in technology. In its early days during the 1980s and 1990s, ETL focused on collecting data from different systems and organizing it for use in centralized databases. It worked in batches, processing large amounts of data at scheduled times, but it struggled with handling unstructured data and was limited to on-site systems.
By the 2000s, as businesses generated more data, ETL tools improved to handle larger volumes efficiently. Automation became more common, and tools like Informatica and Talend made it easier to design workflows visually. However, batch processing was still the standard, and real-time capabilities remained limited.
In the 2010s, cloud computing and real-time data processing transformed ETL. Tools like AWS Glue and Azure Data Factory allowed businesses to process and analyze data as it arrived. These systems became faster and more flexible, supporting data in formats like JSON and XML while significantly reducing infrastructure costs.
In recent years, the rise of big data has further advanced ETL. Modern tools now process massive datasets from diverse sources, including IoT devices and social media feeds. Distributed systems like Hadoop and Spark, along with cloud data warehouses like Snowflake, have made data handling faster and more efficient. Some systems even switched to a process called ELT, where data is transformed after being loaded into storage.
Types of ETL Operations
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) can operate in two primary modes—batch-oriented and real-time. These modes cater to different business needs, offering unique benefits and challenges.
Batch-oriented ETL processes data in groups at scheduled times, such as nightly or weekly. It works well for tasks that do not require immediate updates, like generating financial reports or consolidating sales data. This method is cost-effective and can handle large volumes of data efficiently. However, it has a delay in data availability, making it unsuitable for situations needing instant updates.
In contrast, real-time ETL processes data continuously as it arrives, providing immediate updates. It is ideal for businesses that need up-to-date information, such as fraud detection in transactions or updating live dashboards. Real-time ETL allows quick decision-making and enhances user experiences, but it is more expensive to implement and requires advanced systems to manage constant data flows.
Choosing between batch-oriented and real-time ETL depends on the business’s needs. Batch processing is better for cost-saving and non-urgent tasks, while real-time ETL is necessary for time-sensitive operations and staying competitive in dynamic environments. Many modern tools support both approaches, allowing businesses to adapt as needed.
| Feature | Batch-Oriented ETL | Real-Time ETL |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Scheduled intervals | Continuous or event-driven |
| Latency | High (data is delayed) | Low (near real-time) |
| Complexity | Simpler to set up | More complex |
| Infrastructure Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Use Cases | Historical data analysis | Real-time monitoring and insights |
| Scalability | Limited by batch size | Scales with streaming technologies |
Advantages of ETL
- Easy Data Integration: ETL makes it easier to combine data from different sources, giving a clear and unified view for analysis and decision-making.
- Better Data Quality: The process cleans, organizes, and standardizes data, ensuring it is accurate and reliable for use.
- Advanced Analysis: By preparing and structuring data, ETL supports detailed reporting and analytics.
- Time Saving: Automating ETL processes reduces the need for manual work, making data processing faster and more consistent.
- Scalable: Modern ETL pipelines can scale to match the increasing amounts of data as businesses expand.
Having explored the fundamentals of ETL, in the next section we will understand the basics on Extract, Transform and Load (ELT) process.