OLAP vs OLTP Systems
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) and OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) are two essential approaches in data management, designed to address different needs. While OLTP focuses on handling daily operations efficiently, OLAP is used for analysing data and generating insights to support business decisions. Both play a critical role in maintaining operational performance and enabling strategic analysis
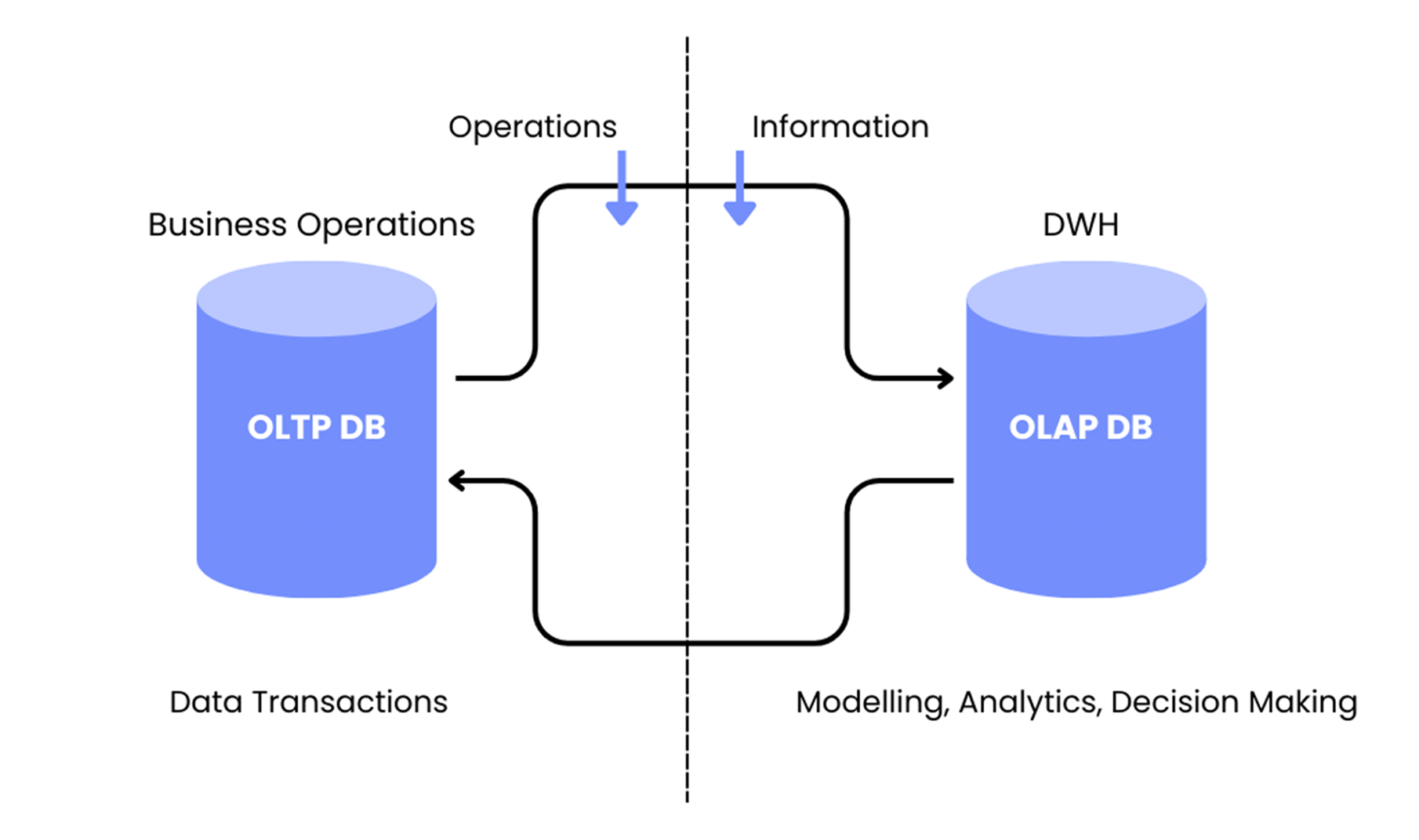
OLTP systems manage the daily operations of a business, like recording sales and updating customer details. Businesses send data from OLTP systems to OLAP systems for analysis. For example, a retail store’s OLTP system processes sales transactions and updates inventory. The OLAP system then analyses this data to find sales trends, predict demand, and assess store performance.
OLTP
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) systems handle the day-to-day operations of a business by processing large numbers of simple transactions. These systems ensure real-time data updates and accuracy, making them essential for tasks like order processing, banking, and inventory management.
Key Features of OLTP
- High Transaction Volume: Processes frequent and straightforward transactions such as data inserts, updates and deletions.
- Real-Time Updates: Ensures current and accurate data for operational use.
- Structured Data: Uses normalized databases to reduce redundancy and maintain efficiency.
OLAP
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) systems enable data analysis and support decision-making. They focus on analysing historical and aggregated data to identify patterns, trends, and insights for long-term planning. A key feature of OLAP systems is the OLAP cube, which allows multi-dimensional analysis, making it easier to slice, dice, and drill down into data across various dimensions.
Key Features of OLAP
- OLAP Cube: A multi-dimensional structure that organizes data into dimensions (e.g., time, location, product) and measures (e.g., sales, profit).
- Complex Queries: Designed for detailed and resource-intensive analytical operations.
- Historical Data: Focuses on past and aggregated data to identify trends and patterns.
- Denormalized Structure: Uses star or snowflake schemas for faster querying.
Differences Between OLTP and OLAP
| Aspect | OLTP | OLAP |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports daily operations and real-time transactions. | Enables analysis and strategic decision-making. |
| Data Type | Current, transactional data. | Historical, aggregated data. |
| Query Type | Short, simple transactions (e.g., INSERT, UPDATE). | Complex, multi-dimensional queries. |
| Database Design | Normalized for efficient storage and updates. | Denormalized for fast querying. |
| Core Structure | Relational database. | OLAP cube for multi-dimensional analysis. |
| Examples | Order processing, banking systems, CRM. | Sales trends, market analysis, forecasting. |
OLAP and OLTP systems both depend on data, but they use it in different ways. OLTP systems handle real-time data from sources like relational databases or APIs. For example, an e-commerce site records customer orders instantly using an OLTP database. On the other hand, OLAP systems pull data from various sources, such as databases, files, or logs, to analyze and provide insights. To make these systems work, we first need to connect to the right datasources. In the next section, we will look at the types of datasources that provide inputs to an OLAP system.