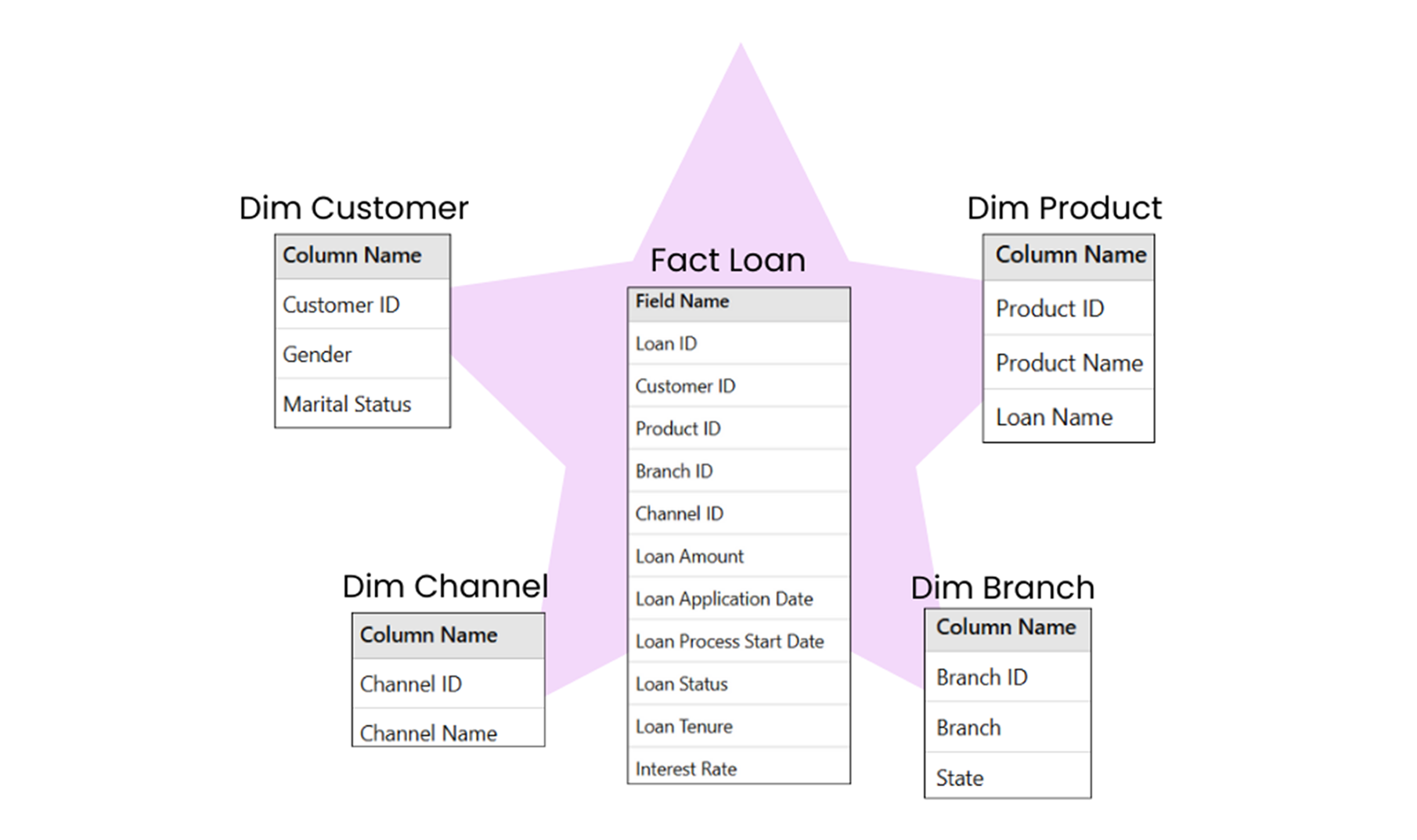
Star Schema
The star schema is a simple and widely used design for organizing data in a data warehouse. It has a central fact table surrounded by multiple dimension tables, creating a star-like structure.
Key Components
- Fact Table: Contains numerical data, such as sales revenue or quantities, and keys that link to dimension tables.
- Dimension Tables: Hold descriptive attributes, such as product names, customer details, or dates, that provide context to the facts.
Characteristics
- Dimension tables are denormalized, meaning data is stored in a flat, easy-to-query format.
- The schema is simple and intuitive, making it easy for non-technical users to query.
Advantages
- Faster query performance due to fewer joins between tables.
- Simpler design and easier to understand for analysts and business users.
- Ideal for business intelligence tools and reporting dashboards.
To create a star schema, start by identifying the business process you want to analyze, such as sales, inventory, or customer behaviour. This process determines the metrics for your fact table, such as revenue, quantity sold, or discounts. The fact table should also include foreign keys that link to the related dimensions.
Next, define the dimension tables. These tables describe the metrics in your fact table with attributes like product name or customer details. Keep all relevant attributes for each dimension in one table to make it easy to query. For example, a customer dimension might include customer ID, name, age, and address.