Stage Tables
Stage tables are temporary tables used during the data loading process in a data warehouse. They act as an intermediate storage area where raw data from various sources is collected, cleaned, and transformed before being loaded into the final tables (fact or dimension tables) of the data warehouse.
Stage tables are typically cleared once the data is successfully loaded onto the warehouse. They store data in its raw form as it is extracted from the source, with minimal initial processing. Their structure often mirrors the source system, with added columns for logging or metadata when needed. These tables are optimized for quick data loading and transformations, making them an essential component of the ETL pipeline.
This area is crucial for consolidating data from different sources, removing duplicates, resolving inconsistencies, and standardizing formats. By handling these tasks separately, the staging area reduces the workload on the main data warehouse and ensures smooth and efficient data processing.
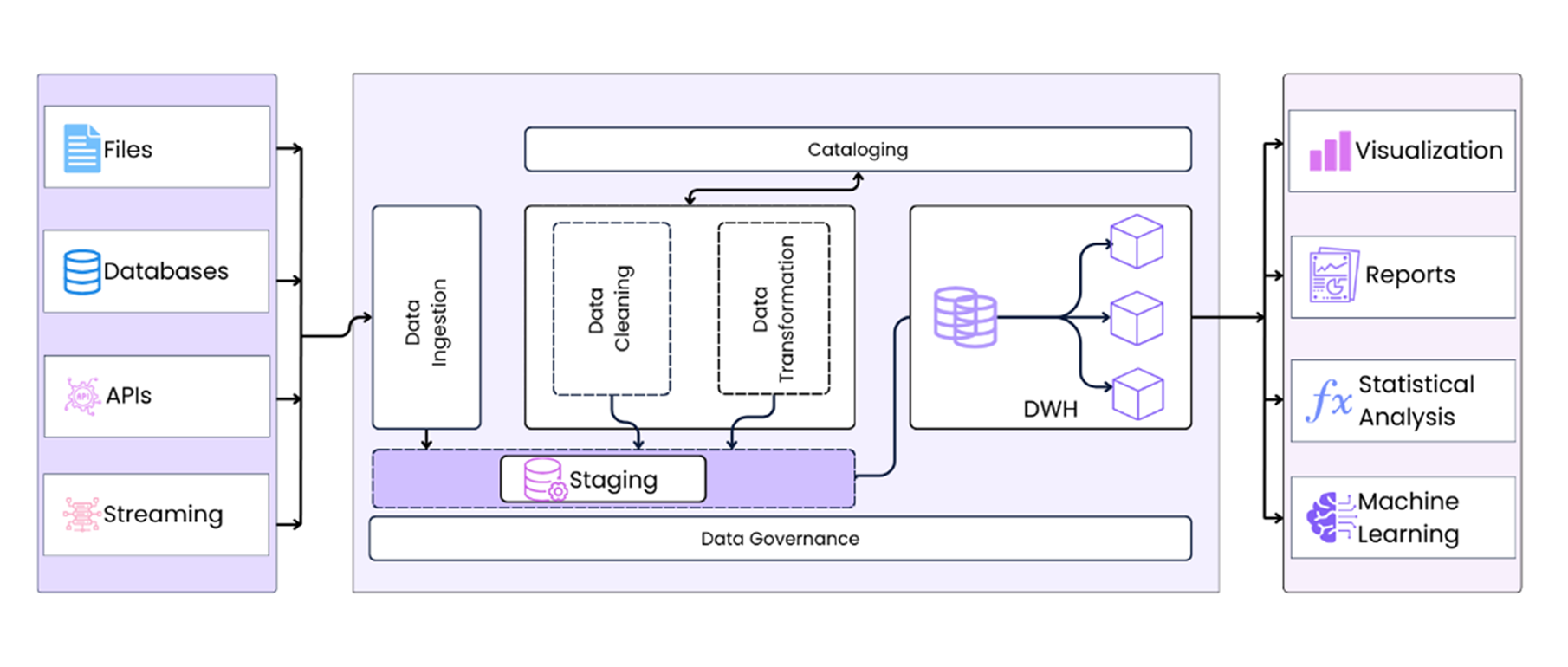
Using stage tables offers several benefits. They ensure high data quality by allowing cleaning and validation before the data reaches the final tables. By separating the extraction process from complex transformations, stage tables make debugging and recovery easier if issues arise. They provide flexibility in handling changes to source data structures without immediately impacting the final schema. Additionally, stage tables optimize performance by processing large volumes of data efficiently.
To make the data staging process efficient, businesses follow key steps:
- Extract data from source systems
- Clean data to remove errors
- Apply transformations for standardization
- Validate data quality
- Load it into the warehouse
The main advantages of a data staging area include improved data quality, reduced workload on the final warehouse, and the ability to handle complex transformations from diverse sources. However, it also has challenges, such as increased system complexity, additional storage requirements, and the need for regular monitoring and maintenance.
Stage tables temporarily hold raw or transformed data before loading it into the data warehouse. They ensure data is cleaned, transformed, validated, and prepared for efficient storage. In the next section, we will explore how data warehousing techniques like Kimball and Inmon use this prepared data to design robust and scalable data warehouses.